Mixture of Experts
·I first time read this paper where Mixture of Experts was used for LLMs in multimodality. And chatgpt gave me the definition of mixture of experts with multimodality as a gatekeeper which decides what modality to choose for the final decision. Like if the audio and video modalities are present then the gatekeeper decides what will decide the final decision of the LLM either audio or images. This gave me the impression that it is like an automatic pruning or more precisely say it is dynamic selection of the modality which decides the output of the LLMs. But how the selection is done. And if the control is actually automatic or manual.
Before starting one of the famous sources for MoE is Maarten Grootendorst’s blog for MoE
Instead of transformers having a heavy (according to parameters wise) feed forward neural network, we have multiple lighter neural networks caller experts. For example there are 64 such experts then only 2 of the experts will be activated of a single input at a time. Thats where the dynamic selection of experts comes.
How it will help selecting the modality? We can train different experts on different modalities and the gating mechanism decide which modality is allowed for the output depending on the gating mechanism weights.so how the gating mechanism is decided? Same as the weights of the neural network are decided with training. The whole system (experts + gate) is trained end-to-end with the main goal as minimizing the loss.The gate learns indirectly: If the gate gives high weight to the wrong expert → task loss goes up. Gradients flow back → gate adjusts its weights to pick the right experts next time. Its just that the gate network is also an FFNN and is used to choose the expert based on a particular input. It outputs probabilities which it uses to select the best matching expert:
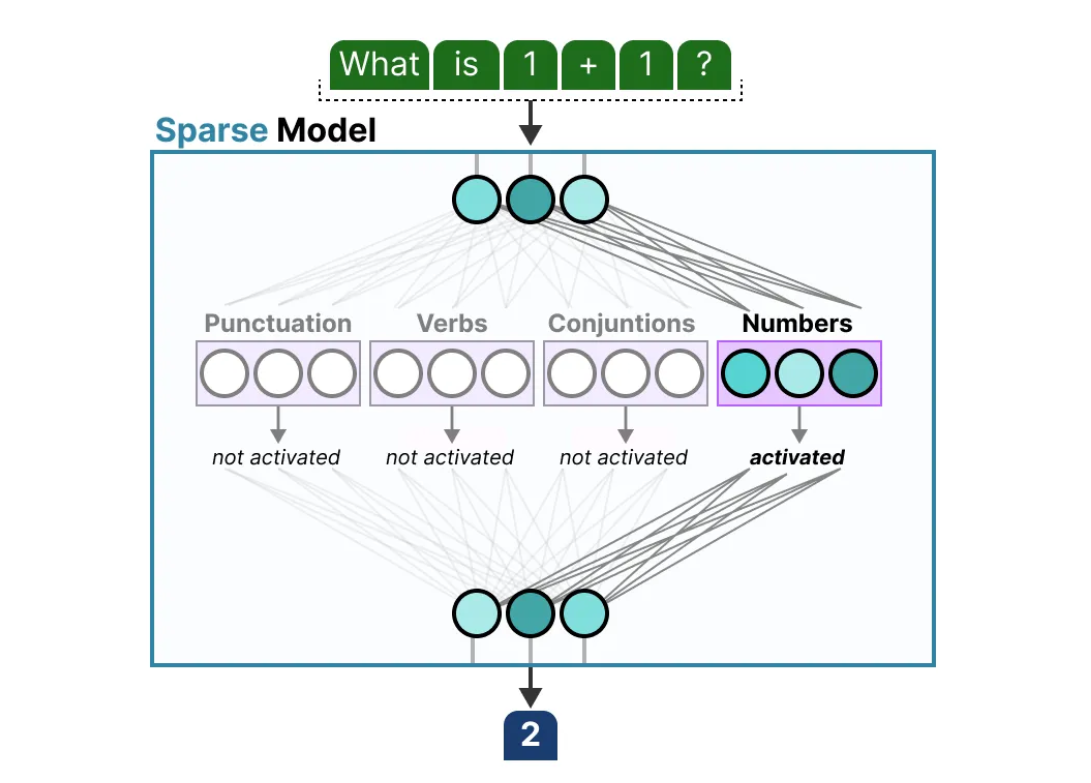
This parameter of dynamic activation of experts through gating mechanism is called regularization or sparsity. There are various techniques on the basis of which the sparsity is controlled :
1) top k gating 2) entropy regularization 3) load balancing loss
Top k gating is when the For Top-k MoE, the gate only routes input to the top 𝑘 experts with highest probabilities. But this makes certain experts prefered all the time, other experts dont get their weights updated. This makes the introduction of load balancing loss.
I want to go in depth in load balancing. It is same as I studied in Wireless Communication. In wireless communication when there is a loads of traffic at a switch and on the basis of priority the data is channelised it is called switching and to deliver different packets to different routers, the gating mechanism is called router.
Imagine a checkout line at a grocery store with 8 checkout lines, only one of which is open. All customers must get into the same line, and therefore it takes a long time for a customer to finish paying for their groceries. Now imagine that the store instead opens all 8 checkout lines. In this case, the wait time for customers is about 8 times shorter (depending on factors like how much food each customer is buying).
Load balancing essentially accomplishes the same thing. By dividing user requests among multiple servers, user wait time is vastly cut down. This results in a better user experience — the grocery store customers in the example above would probably look for a more efficient grocery store if they always experienced long wait times.
So what load balancing in MoE is, compared to load balancing in wireless communication.If only 1–2 experts always get chosen, they get “overloaded” (like one checkout line open).Other experts stay “idle” and they don’t learn, wasting capacity. So the solution is to add load balancing loss to encourage the gate to distribute inputs across experts.
Mathematically, if Ltask is the goal loss then loss is balanced with a factor using load balancing loss Lbalance.
L=Ltask+λ⋅Lbalance
where Lbalance is
Lbalance=M⋅∑fi⋅pi
where fi is the fraction of inputs assigned to expert i and pi is the gate probability of expert i and M is total number of experts.
The main goal of load balancing is to make fi proportional to pi and evenly spread the input to experts.
Now comes what is need of MoE in comparison to attention. There is a paper proposing a MoE Multimodal Graph Attention Network for emotion recognition that combines MoE with graph attention to dynamically integrate audio and visual features with text, demonstrating an alternative to standard fusion methods. Their method sets new state-of-the-art performance in multimodal emotion recognition.
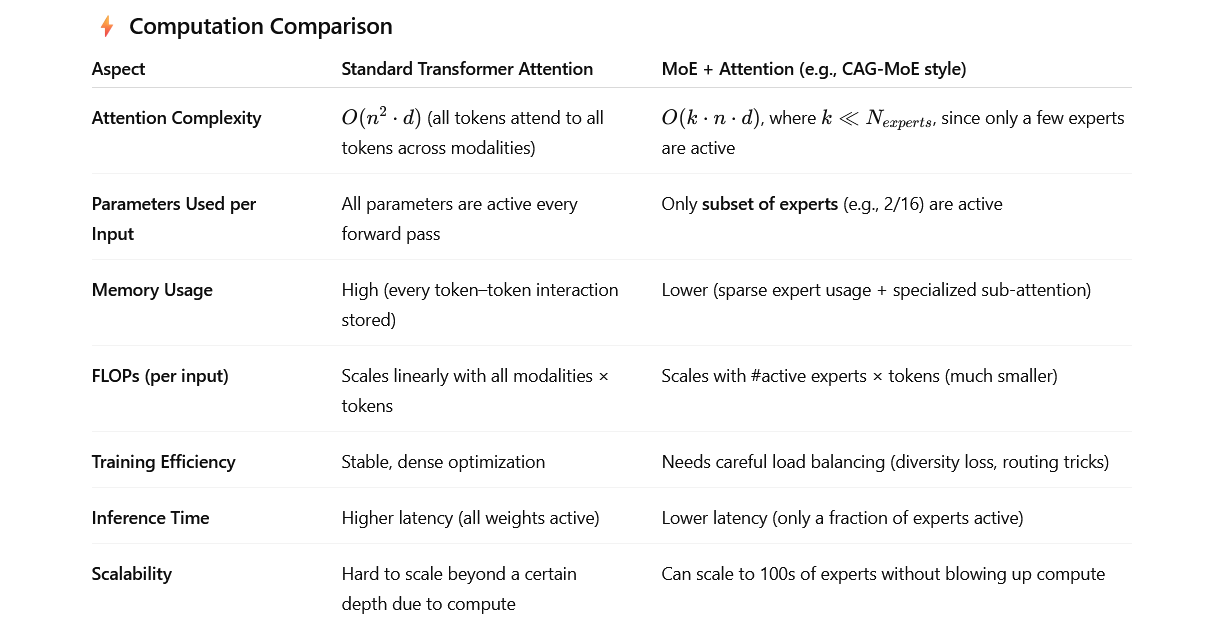
Llama4 preferred the MoE over attention network. One thing is sure that MoE is better than attention network in terms of inference time (memory efficient) and better GPU usage as per FLOPs. Other important advantage of MoE over attention is attention is generalized ie every input goes through same weights…no matter the type (specially in multimodality) but in MoE it is specialized learned where few experts weights are updated as per the input type. The disadvantage of MoE is that bias can creep in because only a few experts dominate the outputs instead of the whole model averaging things out. So MoE can help track the modality bias if text experts are routed more often than audio experts
Llama4 preferred the MoE over attention network. One thing is sure that MoE is better than attention network in terms of inference time (memory efficient) and better GPU usage as per FLOPs. Other important advantage of MoE over attention is attention is generalized ie every input goes through same weights…no matter the type (specially in multimodality) but in MoE it is specialized learned where few experts weights are updated as per the input type. The disadvantage of MoE is that bias can creep in because only a few experts dominate the outputs instead of the whole model averaging things out. So MoE can help track the modality bias if text experts are routed more often than audio experts amd makes it more interpretable in case of multiple modalities.